Last updated: November 7, 2024 at 7:11 AM
Last updated: November 7, 2024 at 7:11 AM
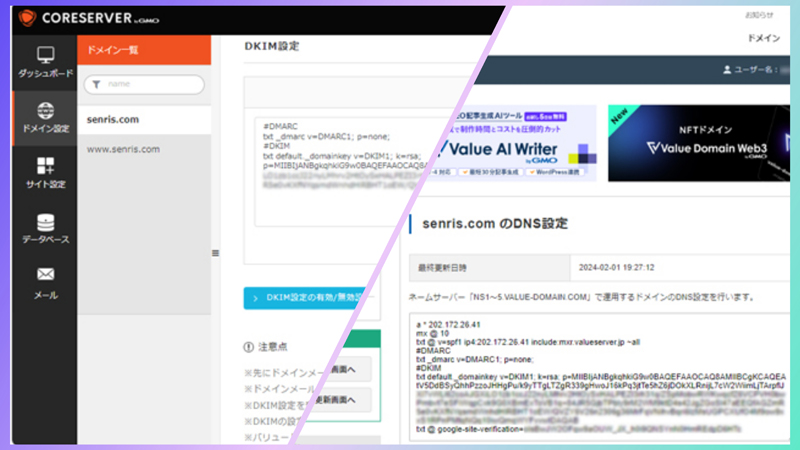
Core Server (GMO Group), which provides rental server services, has started supporting email sending domain authentication technologies "DKIM" and "DMARC" on all servers from February 1, 2024.
With this support, in addition to "SPF" which is already supported on the senris.com server, it is now possible to use "DKIM" and "DMARC" sending authentication technologies, and the following security functions have been strengthened for sent emails. Now you can send and receive emails more securely.
• Reducing the risk of false positive spam emails
• Reduce email security risks such as spoofing
Additionally, the specifications have been changed in response to the recently announced changes to the guidelines for email senders by Google and Yahoo!
[Reference]
• Gmail sender guidelines
• Yahoo! Sender Guidelines
The biggest benefit of these measures is that in addition to eliminating the sending of spam emails pretending to be from our domain (senris.com), it also reduces the risk of false detection of spam emails.
Enabling “DKIM” and “DMARC”
As shown below, all settings were completed by enabling "DKIM" and "DMARC" in the core server settings, and then updating the DNS information in the value domain settings.
After setting up, we also tested sending and receiving from Gmail and Yahoo! mail servers to the senris.com domain to confirm normal operation.
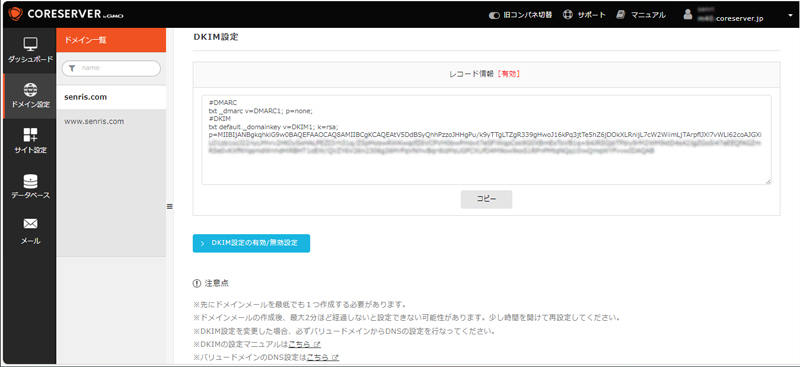
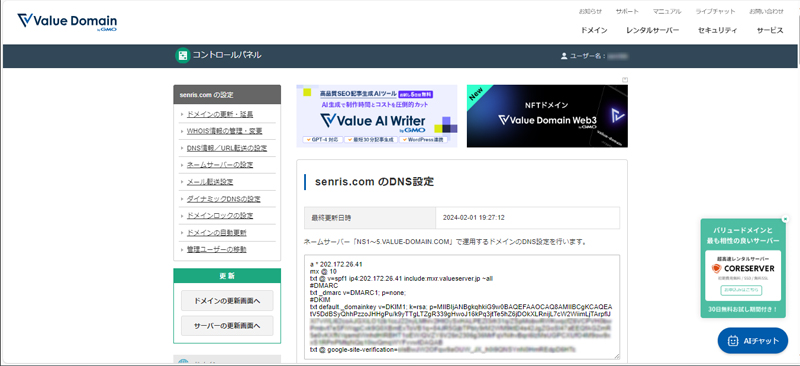
For reference, the manual for enabling "DKIM" and "DMARC" for the domain used on the core server (V1 plan) is as follows.
Glossary What are “SPF”, “DKIM” and “DMARC”?
Each IT term is explained below. Quote source:1 minute explanation of internet terminology – JPNIC
What is SPF?
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is a mechanism to check whether the sender domain of an e-mail is spoofed. The SPF specification is RFC4408*1It is determined by.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), a protocol used for sending emails on the Internet, allows you to freely set the sender's email address (From address). This makes it easy to send ``spoofed email'' that disguises the sender's identity, and this has been used as spam email.
SPF is one of the technologies to prevent spoofing of email addresses, and its feature is that it uses DNS. To make a domain SPF-enabled, include an SPF record in the domain's zone data.*2Add the information. The SPF record describes the IP addresses, etc. of servers that are allowed to send emails from that domain name.
On the other hand, an email receiving server that supports SPF checks the domain from which the email was sent when receiving the email.*3Query DNS for the SPF record of . If the sender's server is not authorized in the SPF record, it is assumed that the sending domain has been spoofed, and processing such as refusing reception is performed.
In other words, SPF is a mechanism that uses the IP address of the sender server and DNS to detect spoofed emails from sources other than the expected sender.As more domains support this mechanism, The effect will be higher.
*1 Sender Policy Framework (SPF) for Authorizing Use of Domains in E-Mail, Version 1
*2 "SPF" is defined in RFC4408 as an RR (resource record) for SPF records, but for programs that cannot handle this, the same RFC also states that the same content should be written in TXT records. Masu.
*3 RFC4408 requires checking the envelope from (email address used in the SMTP MAIL command) and recommends checking the HELO domain (domain name used in the SMTP HELO command). Whether you use it depends on your implementation.
What is DKIM?
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is a sending domain authentication technology for e-mail, and when sending an e-mail, the sender signs an electronic signature and the recipient verifies it, making it possible to impersonate the sender ( This makes it possible to detect email falsification (spoofing) and email falsification.
Sending domain authentication technologies can be broadly divided into those that use the sender's IP address and those that use electronic signatures. DKIM uses electronic signatures, and the public key required to verify the electronic signature is Published on the sending domain's DNS server. The recipient identifies the domain from the information about the signer in the email they receive, and obtains the public key by querying the DNS server.
Creating an electronic signature does not necessarily have to be done by the sender himself, but can be done by the email relay server (MTA), sending mail server (MSA) used by the email sender, or a trusted third party. . By taking advantage of these features, you can, for example, configure the email server to create electronic signatures and transparently add signatures using DKIM to end users' emails.
Recently, an email authentication technology called DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance), which combines SPF (Sender Policy Framework), which uses the sender's IP address, and DKIM, has been introduced in the same sending domain authentication technology. As a result, DKIM is becoming more popular.
■Reference
RFC 6376 – DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) Signatures
RFC 6377 – DKIM And Mailing Lists
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
What is DMARC?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is a sending domain authentication technology for email, and is based on RFC 7489.*1is standardized.
Technologies used for sending domain authentication include SPF (Sender Policy Framework).*2or DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)*3there is. The former, SPF, is a means of determining whether the IP address of the sender's mail server is legitimate. The latter, DKIM, adds an electronic signature to emails, making it possible to verify that the sender and content of the email have not been tampered with. DMARC is a technology that strengthens email domain authentication using both.
When authenticating a sending domain using SPF and DKIM, it is up to the recipient to decide what to do with emails that fail authentication. In addition, the sender has no way of knowing that authentication failed or how the email was processed.
DMARC was proposed to augment the behavior of SPF and DKIM. DMARC has a mechanism in which the sender declares to the recipient how to handle the email in the event of an authentication failure by publishing a record called a policy on DNS. If authentication fails, the recipient refers to the sender's policies and uses them to decide what to do with the email.
Furthermore, DMARC allows the recipient to send a report to the sender notifying the sender that authentication has failed. By examining the contents of the report sent by the recipient, the sender can use it to determine whether their own email system is operating correctly and to take measures against spam mail.
*1 RFC7489: Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC)
*2 RFC7208: Sender Policy Framework (SPF) for Authorizing Use of Domains in Email,Version 1